-
public interface PlatformDependenciesPlatform Dependencies
Client-side processing of web services, XML parsing, and some UI loading mechanisms rely on a native in-browser XML parser and/or the XMLHttpRequest object - one or both of which will not be available if the end user disables ActiveX support in Internet Explorer. Note that these features do not require plugins or downloads of any kind - IE simply exposes certain built-in functionality like the XML parser and XMLHttpRequest through the ActiveX interface. Disabling ActiveX also disables all browser plugins such as Flash, Java, SVG, etc.Barring ActiveX being disabled, the XMLHttpRequest object is available to Smart GWT on all supported browsers and an XML parser is available on all supported browsers except Safari versions prior to 3.0.3.
Smart GWT client-server communication is not affected by the lack of an XML parser or the XMLHttpRequest object, but the
xmlHttpRequesttransport will not be available if the XMLHttpRequest object is not available. Instead, thehiddenFrameor thescriptIncludetransports are used for client-server communication.XML Parser
If an XML Parser is not available to Smart GWT, all client-side web service bindings and related methods will be unavailable. Turning off ActiveX disables integration paths 2 and 3 in the diagram below. If you want to bind to web services and require deployment to IE without ActiveX (or you need to support Safari pre 3.0.3), you'll need to do all XML processing on the server and use either the Smart GWT DSRequest or JSON operation pathways (integration paths 1 and 4 in the diagram below). See the discussion in
ClientServerIntegrationfor more information on the integration paths shown in the diagram below.You call
XMLTools.nativeXMLAvailable()to check for the availability of a native XML parser at runtime.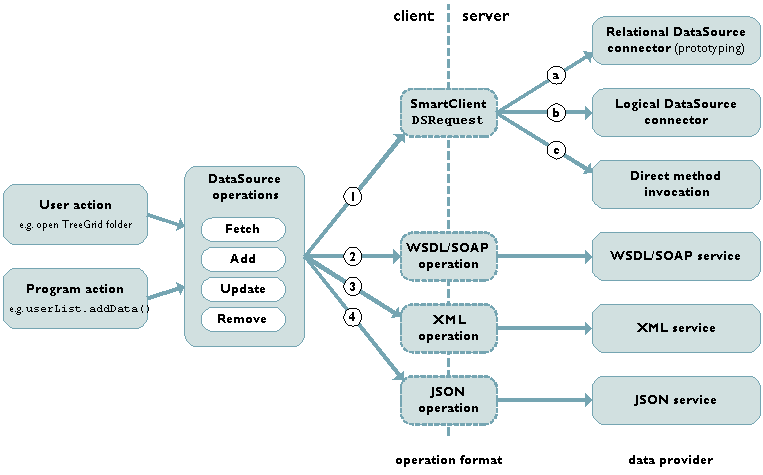
XMLHttpRequest
The XMLHttpRequest object is used for the
xmlHttpRequestRPCTransport. Safari, Mozilla, Firefox, and IE 7 provide a native XMLHttpRequest implementation that is not affected by ActiveX being disabled (although the native IE 7 implementation can still be explicitly disabled by the end user). IE 5.5 and IE 6.0 rely on the ActiveX bridge to support XMLHttpRequest, so if ActiveX is disabled in these browsers, XMLHttpRequest will not be available.The lack of the XMLHttpRequest objects affects UI loading features like
ViewLoader, andHTMLFlowwhen used in remote loading mode (viaHTMLFlow.contentsURL,HTMLFlow.setContentsURL(), but does not affect the typical client/server communication pathways (integration paths 1 and 5 in the diagram above).Also affected are low level features
RPCRequest.serverOutputAsString,RPCRequest.evalResult, andRPCResponse.httpResponseCode.In all of the above cases, it is possible to use the
hiddenFrametransport to support these features when XMLHttpRequest is not available. Smart GWT will automatically send the request using thehiddenFrametransport when it detects that XMLHttpRequest is unavailable. To support the above features, you'll need to use the RPCManager APIs on the server to send back the data that would normally be returned by XMLHttpRequest. Since XMLHttpRequest cannot target URLs outside of the current domain, this strategy applies also to using the above features with cross-domain URLs.You can call
RPCManager.xmlHttpRequestAvailable()to check for the availability of XMLHttpRequest at runtime.